By: Bennett Hara
Updated By: Dr. Caitlin Solone
Updated Introduction from Caitlin Solone, PhD
There is often confusion between the Special Olympics and the Paralympics, as both organizations offer athletic opportunities for individuals with disabilities. However, each serves a unique purpose and caters to different groups of athletes.
The Special Olympics serves athletes with intellectual disabilities and generally includes participants aged 8 years and older, though some programs, like the Young Athletes program, involve children as young as 2. The organization's philosophy emphasizes inclusivity, advocating for the "power of sport to help all who participate fulfill their potential." Unlike other competitive arenas, the Special Olympics allows participation regardless of skill level or qualifying scores, fostering a supportive environment for personal growth and development. Competitions occur at local and international levels, with World Games held every two years, alternating between Summer and Winter and selection for the Games is random from the eligible athletes.
The Paralympics focuses on elite athletes with physical, visual, and intellectual disabilities and is run in parallel with the Olympic Games. These athletes undergo rigorous training and must meet strict qualification standards through international competitions or specific performance criteria. The Paralympic Games, held every two years shortly after the Olympic Games (both Summer and Winter), share the same venues as the Olympics. The Paralympics feature 28 sports, showcasing elite high-performance competition. The selection process is highly competitive, requiring athletes to achieve minimum qualifying standards nationally and internationally.
Both the Special Olympics and Paralympics strive to enhance the lives of individuals with disabilities through sport, though they differ in scope, audience, and competitive level. The Special Olympics is headquartered in Washington D.C., while the Paralympics are governed by the International Paralympic Committee, headquartered in Bonn, Germany.
Below the Special Olympics vs. Paralympics facts are presented in three equivalent versions depending on preference: infographic, HTML table, and text with subheading organization.
Infographic
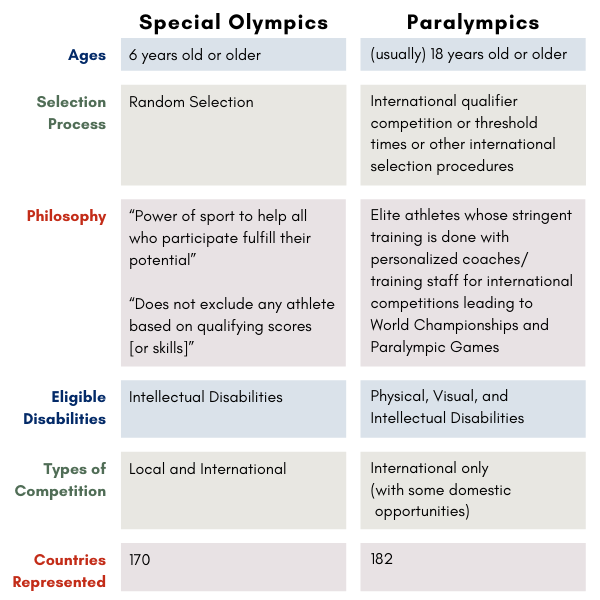
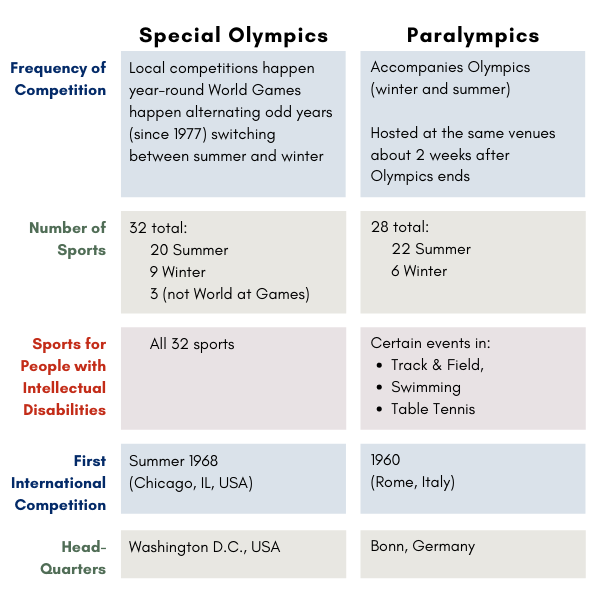
The Paralympics and Special Olympics often get confused with one another. Here is a chart to highlight the main differences between these sports organizations.
Visual
Note: Minimum age for Special Olympics has been updated to 8. There is a young athletes program for 2-7 year olds.
Both of these organizations create platforms for people with disabilities to be able to compete in sports but they differ in their intentions. While the Paralympics values competition and elite skill levels, the Special Olympics values the power sports has to allow people to reach their full potential.
HTML Table
See below for an accessible HTML table of the information instead:
| Topic | Special Olympics | Paralympics |
|---|---|---|
| Ages | 8 years old or older | (usually) 18 years old or older |
| Selection Process | Random Selection | International qualifier competition or threshold times or other international selection procedures |
| Philosophy | “Power of sport to help all who participate fulfill their potential” “Does not exclude any athlete based on qualifying scores [or skills]” | Elite athletes whose stringent training is done with personalized coaches/ training staff for international competitions leading to World Championships and Paralympic Games |
| Eligible Disabilities | Intellectual Disabilities | Physical, Visual, and Intellectual Disabilities |
| Types of Competition | Local and international | International only (with some domestic qualifying opportunities) |
| Frequency of Competitions | Local competitions happen year-round World Games happen alternating odd years (since 1977) switching between summer and winter | Accompanies Olympics (winter and summer) Hosted at the same venues (about 2 weeks after Olympics ends) |
| Number of Sports | 32 total: 20 Summer, 9 Winter, 3 (not at World Games) | 28 total: 22 Summer & 6 Winter |
| Sports for People with Intellectual Disabilities | All 32 sports | Certain events in: Track & Field, Swimming & Table Tennis |
| Countries Represented | 170 | 182 |
| First International Competition | Summer 1968 (Chicago, IL, USA) | 1960 (Rome, Italy) |
| Headquarters | Washington D.C., USA | Bonn, Germany |
Information in Text Format
Age Requirements
Special Olympics: 8 years or older (There is a young athletes program for aged 2-7)
Paralympics: (usually) 18 years or older
Selection Process
Special Olympics: Random Selection
Paralympics: International qualifier competition, threshold times or other international selection procedures
Philosophy
Special Olympics: “Power of sport to help all who participate fulfill their potential”; “Does not exclude any athlete based on qualifying scores [or skills]”
Paralympics: Elite athletes whose stringent training is done with personalized coaches/training staff for international competitions leading to World Championships and Paralympic Games
Eligible Disabilities
Special Olympics: Intellectual Disabilities
Paralympics: Physical, Visual, and Intellectual Disabilties
Types of Competition
Special Olympics: Local and International
Paralympics: International only (with some domestic qualifying opportunities)
Frequency of Competition
Special Olympics: Local competitions happen year-round World Games happen alternating odd years (since 1977) switching between Summer and Winter
Paralympics: Accompanies Olympics (Summer and Winter); hosted at the same venues about 2 weeks after Olympics ends
Number of Sports
Special Olympics: 32 total: 20 Summer, 9 Winter, 3 Not at World Games
Paralympics: 28 total: 22 Summer & 6 Winter
Sports for People with Intellectual Disabilities
Special Olympics: All 32 sports
Paralympics: Certain events in: Track & Field, Swimming & Table Tennis
Countries Represented
Special Olympics: 170
Paralympics: 182
First International Competition
Special Olympics: Summer 1968 (Chicago, IL, USA)
Paralympics: 1960 (Rome, Italy) - Previously the Stokes Mandeville Games started in 1948
Headquarters
Special Olympics: Washington D.C., USA
Paralympics: Bonn, Germany
Sources:
- https://www.paralympic.org/
- http://media.specialolympics.org/soi/files/press-kit/SO-andPARALYMPICS_2014_FactSheet_Final.pdf
Originally Posted: 21 May 2020
Updated: 7 August 2024